|
(11) | EP 0 214 939 A2 |
| (12) | EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (54) | Padding material for use in clothing or furnishings |
| (57) A padding material of synthetic fibres having a high degree of thermal insulation
and usable advantageously in the field of clothing and furnishing comprises a base
layer (1) obtained by carding a mixture of polyester fibres which have been treated
with a mixture of adhesive resins of plastic consistency which, when polymerised,
create a very soft and elastic film and then subsequently, calendering the layer in
such a way as to reduce its initial thickness, the base layer (1) having on one or
both sides thereof a cladding layer (2) constituted by a resin, preferably polyurethane,
based on aromatic polyaters dissolved in solvent. The cladding layer (2) itself may further have a very light finishing layer (3) applied thereto, this finishing layer (3) being based on acrylic polymers or copolymers dissolved in organic solvents modified with cellulosic resins such as cellulose acetyl butyrate and may have slip agents and anti blocking substances added thereto. |
[0001] The present invention relates to a padding material composed of synthetic fibres which padding material can be formed into relatively thin layers whilst retaining a high degree of thermal insulation. Such padding is of particular utility in the fields of clothing and furnishings.
[0002] There are at present commercially available paddings based on layers of wadding, generally made of synthetic fibres, and used as insulating materials. It is known that padding materials utilised for clothing and furnishings and the like must preferably have a limited thickness for aesthetic reasons, but must retain a high degree of thermal insulation.
[0003] The present invention seeks therefore to provide a padding material having significantly improved thermal insulation characteristics in a product which will be more compact and manageable, and thus more easily used in the field of clothing and furnishings and the like.
[0004] It is important, however, that a padding material having such qualities should, as well as having high thermal insulation, also have qualities of softness, elasticity and pleasantness to the touch, which are typical of padding materials generally.
[0005] According to the present invention, there is provided a padding material with high degree of thermal insulation, for use in clothing, furnishing or the like, comprising a base layer obtained by carding a mixture of fibres, including polyester fibres, with siliconised fibres which have been treated with a mixture of adhesive resins of sticky, plastic consistency, which are then polymerised to create a soft, elastic film, this base layer being subsequently subjected to calendering in such a way as to reduce its initial thickness, characterised by the fact that a layer of cladding materials is applied to one or both sides of the said resin treated base layer.
[0006] An advantage of the padding material of the present invention is that as well as presenting characteristics of significantly improved insulation, it is more easily workable than similar commercially available paddings, and still has aesthetically desirable properties of handle and flexibility.
[0007] The cladding layer is preferably a polyurethane based on aromatic polyesters dissolved in a solvent.
[0008] Furthermore, a very light, thin finishing layer may be applied over the said cladding layer. The said finishing layer is preferably based on acrylic polymers or copolymers in organic solvents modified with cellulosic resins - (cellulose acetyl butyrate) - and having additional slip agents and anti blocking substances.
[0009] One embodiment of the present invention will now be more particularly described by way of example, with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a sectional side view of a starting layer;
Figure 2 is a sectional side view of the same layer after the application to one of its faces of a cladding layer; and
Figure 3 is a sectional side view of the same layer carrying a finishing layer on one of the said cladding layers.
[0010] With reference now to the attached drawing, the padding shown comprises a layer 1 formed by a mixture of fibres of polyester, or of other nature (including natural fibres), which may be treated with silicone, and subjected to carding and subsequent calendering processes.
[0011] Onto one or both sides of the layer thus obtained there is applied a cladding layer 2 the thickness of which lies between 5 and 20 microns. This cladding layer 2 is made of a material having a high degree of thermal insulation and significant elasticity in such a way as not to prejudice the characteristics of elasticity and softness of the padding layer itself and its properties of insulation and transpiration, but at the same time improving the characteristics of workability in the manufacturing stages of the finished products.
[0012] Preferably the said cladding layer 2 is constituted by a polyurethane resin based on aromatic polyesters dissolved in a solvent or solvents. In particular, the choice of the type of resin is related to the properties required by the conditions of use of the finished product. In fact, its mechanical properties must include good elasticity, resistance to tension, and resistance to abrasion, and its chemical properties must include resistance to light and resistance to washing among others.
[0013] The preferred characteristics of the said cladding layer, in practice, can be listed as follows:-Mechanical characteristics:
[0016] Over the said cladding layer there may be applied a further very light finishing layer 3 the presence of which improves the properties of the padding, namely the presentation, handle, workability and the like, as well as its characteristics of insulation and impermeability, without, however, detrimentally affecting the transpiration ability of the padding layer as a whole.
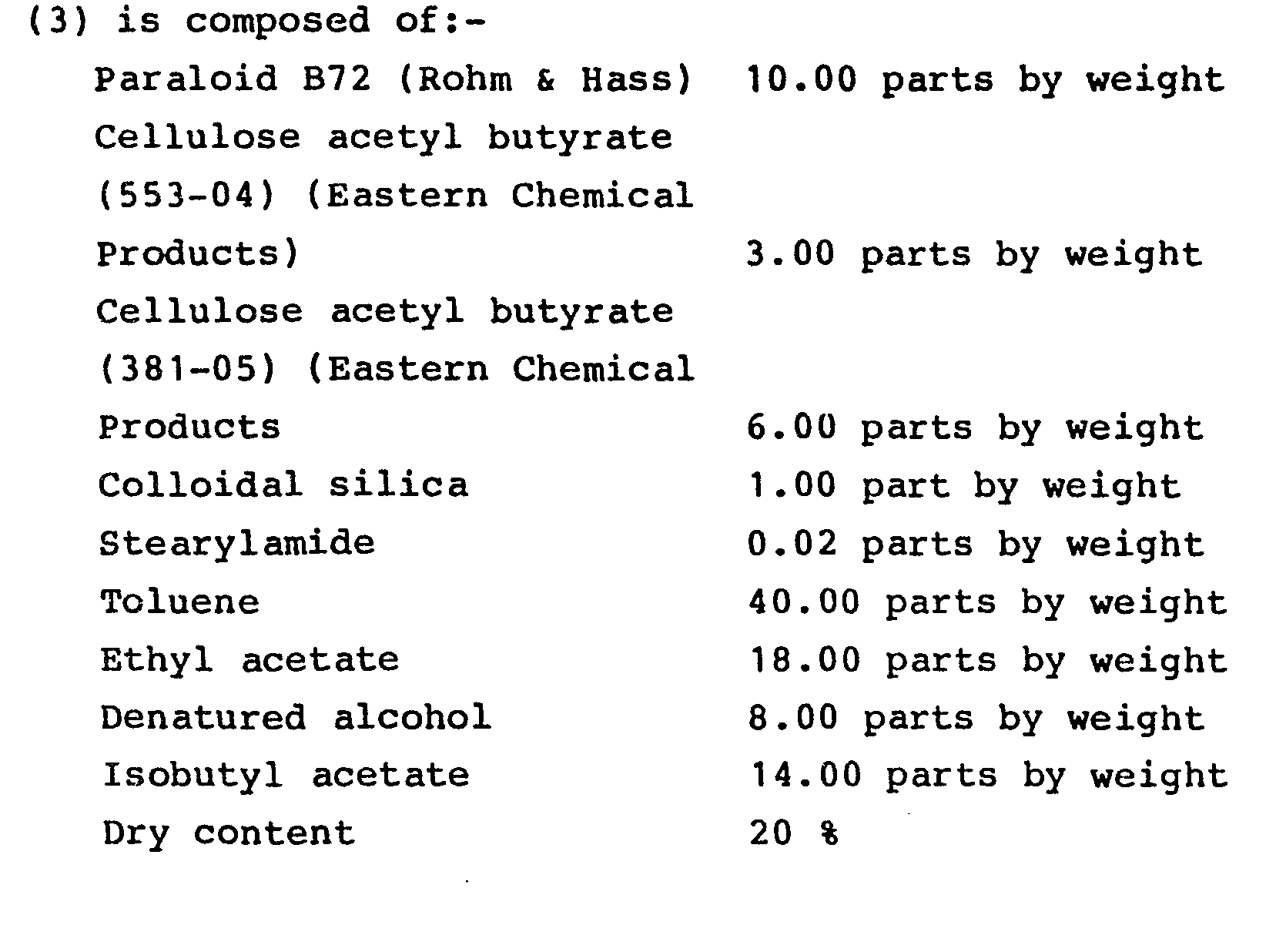
[0017] The composition of this finishing layer 3 is in general based on acrylic polymers or copolymers in organic solvents, modified with cellulosic resins (cellulose - acetyl butyrate) with the addition of slip agents and anti blocking substances.
[0018] Hereinbelow is given a typical example, purely by way of indication, of a suitable composition for the said finish layer 3.
[0019] The said cladding layer 2 and finishing layer 3 are applied to the layer 1 generally by means of spreading or preferably, by means of so-called "transfer"
[0020] spreading techniques, which are processes of known type. Preferably "transfer" spreading is used as this permits more brilliant results to be obtained and has more controllable and reproduceable operating conditions.
[0021] In particular, in dependence on the availability of the equipment, the said finishing layer 3 can be applied subsequently to the product by means of rotographic or flexographic printing, starting from a suitably adapted solution. In practice, the application onto the base layer 1 of the said cladding layer 2 and the said surface finish layers 3 forms a barrier layer which is effectively impermeable to air from the outside, but such as not to impede transpiration. These cladding layers 2, 3 are conveniently elastic and soft and are able to permit any condensation which forms inside the padding layer to escape thus contributing to an improvement in the hygiene characteristics of the product.
1. A padding material with high degree of thermal insulation, for use in clothing,
furnishing or the like, comprising a base layer (1) obtained by carding a mixture
of fibres, including polyester fibres, with siliconised fibres which have been treated
with a mixture of adhesive resins of sticky, plastic consistency, which are then polymerised
to create a soft, elastic film, this base layer (1) being subsequently subjected to
calendering in such a way as to reduce its initial thickness, characterised by the
fact that a layer of cladding materials (2) is applied to one or both sides of the
said resin treated base layer.
2. A padding material according to Claim 1, characterised by the fact that the said
resin is a polyurethane based on aromatic polyesters dissolved in one or more solvents.
3. A padding material according to Claim 1 or Claim 2, characterised by the fact that
over the said cladding layer (2) there is further applied a very light finishing layer
(3).
4. A padding material according to Claim 3, characterised by the fact that the said
finish layer (3) is constituted by acrylic polymers or copolymers in organic solvents
modified with cellulosic resins to which has been added slip agents and anti blocking
substances.
5. A padding material according to any preceding Claim, characterised by the fact
that the said cladding layer (2) applied to the said resin treated base layer (1)
has a thickness lying between 5 and 20 microns and is constituted by a polyurethane
resin based on aromatic polyesters dissolved in solvents.
6. A padding material according to any preceding Claim, characterised by the fact
that the solution utilised for the or each of the said cladding layers (2) is composed
of:

7. A padding material according to any of Claims 3 to 6, characterised by the fact
that the said finish layer
8. A padding material according to any preceding Claim, characterised by the fact
that the said cladding layer or layers-(2) and the said finishing layer or layers
(3) is or are applied to the said base layer (1) by the techniques of spreading, or
"transfer" spreading known per se.
9. A padding material according to any of Claims 3 to 8, characterised by the fact
that the said finishing layer (3) is applied subsequently to the product by means
of rotographic or flexographic printing, using a suitably adapted solution.
