|
(11) | EP 2 925 711 B1 |
| (12) | EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION |
|
|
| (54) |
SYNTHESIS OF TETRAHYDROMYRCENOL SYNTHESE VON TETRAHYDROMYRCENOL SYNTHÈSE DE TÉTRAHYDROMYRCENOL |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note: Within nine months from the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to the European patent granted. Notice of opposition shall be filed in a written reasoned statement. It shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). |
[0001] The present invention relates to a new and improved synthesis of tetrahydromyrcenol (IUPAC name: 2,6-dimethyl-2-octanol).
[0002] Tetrahydromyrcenol (CAS Number: 18479-57-7), which is the following compound of formula (I)
is a well-known compound in the flavour and fragrance industry. It used widely for many applications. It is described olfactory as "fresh, overall citrus-floral and sweet odour with terpenic undertones".
[0003] A process for preparing tetrahydromyrcenol by hydrogenation of the alloocimenol isomers I and II is described in DE 11 18 190. Due to the importance of tetrahydromyrcenol, there is always a need for an improved process for its production.
[0004] We found that that the reductive ring opening of a compound of formula (II)
results in an excellent selectivity and yield of tetrahydromyrcenol.
[0005] It is surprising that the reductive ring opening does not result (or only in minimal amounts) in undesired side products such as i.e.
[0006] Furthermore it is surprising that the ring opens selectively at the "correct" position (position 2; which leads to tetrahydromyrcenol) and not at position 6. Such a ring opening would lead (for example) to a compound of formula (VI)
[0007] Compound of formula (VI) is not found in the reaction mixture at the end of the synthesis, as well as other possible reaction products from such ring opening are not found.
[0008] Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I)
by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II)
[0009] The compound of formula (II) can, for example, be prepared from dehydrolinalool by ring closure catalysed by tungsten, molybdenum or polyphosphoric acid (Strickler et al., Helv. Chem. Acta 1966 , 49, 2055; Erman et al., Tetrahedron 1976, 34, 2981, and Belgian Patent No. 852 918).
[0010] The reduction agent used in the process according to the present invention is preferably H2 gas.
Therefore the process according to the present invention is preferably carried out under pressure.
[0011] Usually the pressure is at least 1 bar, preferably at least 3 bars.
A preferred range for the pressure under which the process according to the present invention is carried out, is 1 - 20 bar, more preferably 3 - 15 bar.
All the pressures given in the context of the present patent application are always absolute pressures.
[0012] Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out with H2-gas at a pressure of 1 - 20 bar, preferably at 3 - 15 bar.
[0013] The process according to the present invention is usually carried out at temperatures from 15 - 100 °C, preferably from 20 - 80°C.
[0014] Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C.
[0015] Preferably the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out with H2-gas at a pressure of 1 - 20 bar, preferably at 3 - 15 bar and at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C.
[0017] Preferably the process according to the present invention is carried out in an inert solvent (or a mixture of solvents). Inert solvent means that the solvent will not take part in the reaction process.
[0018] The solvent must be liquid at the reaction condition used in a process according to the present invention.
[0019] Suitable solvents are i.e. alcohols (such methanol, ethanol), hydrocarbons (such as n-hexane, n-heptane), esters, ethers (such as THF), chlorinated hydrocarbons (such as CH2Cl2).
[0020] Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out in a solvent or in a mixture of solvents (preferably alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters, ethers and chlorinated hydrocarbons).
[0021] Preferably the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out
with H2-gas at a pressure of 1 - 20 bar, preferably at 3 - 15 bar and at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C
and a solvent or in a mixture of solvents (preferably alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters, ethers and chlorinated hydrocarbons).
[0022] Preferably the process according to the present invention is carried out in the presence of a catalyst.
[0023] The catalyst is a transition metal on a support material. Usually the support material is carbon or a solid acid. Preferred transition metals are Pt, Rh and Pd,
More preferred is palladium on carbon (Pd/C). Such a catalyst (CAS number of 7440-05-3) is commercially available for example from Sigma Aldrich.
[0024] Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out is carried out in the presence of a catalyst (preferably a transition metal on a support material, more preferably Pd/C). Preferably the catalyst is present in the process in amount of up to 10 wt-% (based on the weight of compound of formula (II)), more preferably up to 5 wt%.
Preferably the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out
with H2-gas at a pressure of 1 - 20 bar, preferably at 3 - 15 bar, and at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C, and a solvent or in a mixture of solvents (preferably alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters, ethers and chlorinated hydrocarbons), and
in the presence of up to 10 wt-% (based on the total weight of compound of formula (II)) of at least one catalyst (preferably a transition metal on a support material, more preferably Pd/C), preferably up to 5 wt%.
[0025] The process according to the present invention is usually carried out in the presence of an acid. The acid can be organic as well as inorganic (as well as mixtures). Suitable acids are i.e. HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid. It is also possible to use solid acids.
[0026] Preferably the acid is present in an amount of 1 - 20 wt-% (based on the total weight of compound of formula (II))
Therefore the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out is carried out in the presence of an organic and/or an inorganic acid, as well as mixtures thereof (preferably HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid).
[0027] Preferably the present invention relates to a process for production of compound of formula (I) by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II), characterized in that the reaction is carried out
with H2-gas at a pressure of 3 - 20 bar, preferably at 3 - 15 bar, and at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C, and
a solvent or in a mixture of solvents (preferably alcohols, hydrocarbons, esters, ethers and chlorinated hydrocarbons), and
in the presence of a catalyst (preferably a transition metal on a support material, more preferably Pd/C), and
in the presence of an organic and/or an inorganic acid, as well as mixtures thereof (preferably HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid).
[0028] The following examples illustrate the present invention.
All the parts and percentages in the Examples are related to the weight (when not otherwise stated) and the temperature is given in °C (when not otherwise stated).
Examples
Example 1:
[0029] 8 mg of the catalyst (Pd/C) was added to a 8 ml glass reactor and 2-ethynyl-2,6,6-trimethyl-tetrahydropyran (210 mg, 95%) was added. Heptane (1.5 g) and concentrated hydrochloric acid (10 µl) were added and the reactor was sealed. The reactor was purged with argon 3 times (by pressurising to 5 bar followed by release of the pressure) and 3 times with hydrogen (pressurise to 5 bar then release). The reaction mixture was heated to 50 °C, pressurised to 10 bar hydrogen and stirred until no more hydrogen consumption was observed and then for a further 30-60 minutes. The stirring was stopped and the reaction allowed to cool to room temperature.
[0030] The pressure was released and the reactor purged 2 times with argon. After filtration to remove the catalyst, the reaction mixture was analysed by GC to determine conversion and selectivity.
The selectivity and the yield was more than 90 %.
[0031] The examples in the following table have been synthesised in analogy to example 1. The amount of catalyst, the acid, the amount of acid, the pressure and the reaction temperature have been varied.
Table 1:
| Exp. | Solvent | Amount Cat [mg] | Acid | Amount acid | p [bar] | T [°C] | Yield [%] |
| 2 | THF | 14 | HCl | 10 µl | 10 | 50 | 68 |
| 3 | n-heptane | 17 | HCl | 10 µl | 10 | 50 | 78 |
| 4 | n-heptane | 23 | HCl | 10 µl | 10 | 30 | 78 |
| 5 | n-heptane | 26 | HCl | 10 µl | 3 | 50 | 74 |
| 6 | n-heptane | 9 | HCl | 10 µl | 3 | 70 | 87 |
| 7 | n-heptane | 10 | p-toluenesulfonic acid | 11 mg | 10 | 50 | 50 |
1. A process for production of compound of formula (I)
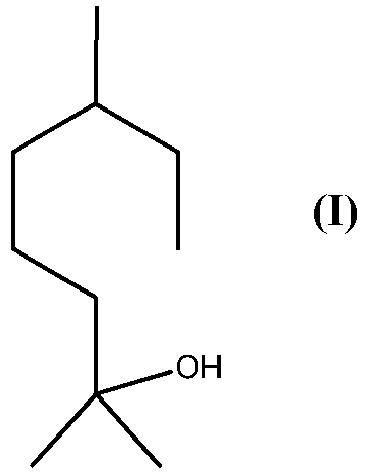
by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II)

by a reductive ring-opening of a compound of formula (II)
2. Process according to claim 1, wherein the reducing agent is H2 gas.
3. Process according to claim 2, wherein process is carried out under pressure of at
least 1 bar, preferably at least 3 bars.
4. Process according to any of the preceding claims, wherein the process is carried out
at temperatures from 15 - 100°C, preferably from 20 - 80°C.
5. Process according to any of the preceding claims, wherein the process is carried out
with or without a solvent.
6. Process according to any of the preceding claims, wherein the process is carried out
in the presence of a catalyst (preferably a transition metal on a support material,
more preferably Pd/C).
7. Process according to any of the preceding claims, wherein the process is carried out
in the presence of an acid (preferably HCl, H2SO4, p-toluenesulfonic acid).
1. Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Verbindung der Formel (I)
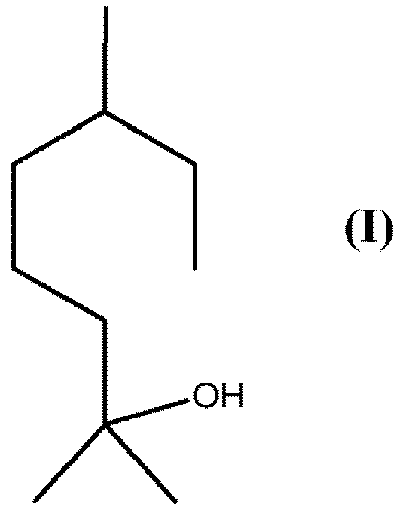
durch reduktive Ringöffnung einer Verbindung der Formel (II)

durch reduktive Ringöffnung einer Verbindung der Formel (II)
2. Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, bei dem es sich bei dem Reduktionsmittel um H2-Gas handelt.
3. Verfahren nach Anspruch 2, das unter einem Druck von mindestens 1 bar, vorzugsweise
mindestens 3 bar, durchgeführt wird.
4. Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, das bei Temperaturen von 15-100°C,
vorzugsweise von 20-80°C, durchgeführt wird.
5. Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, das mit oder ohne Lösungsmittel
durchgeführt wird.
6. Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, das in Gegenwart eines Katalysators
(vorzugsweise eines Übergangsmetalls auf einem Trägermaterial, weiter bevorzugt Pd/C)
durchgeführt wird.
7. Verfahren nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, das in Gegenwart einer Säure (vorzugsweise
HCl, H2SO4, p-Toluolsulfonsäure) durchgeführt wird.
1. Procédé de production d'un composé de formule (I)

par une ouverture de cycle réductrice d'un composé de formule (II)

par une ouverture de cycle réductrice d'un composé de formule (II)
2. Procédé selon la revendication 1, où l'agent réducteur est du H2 gazeux.
3. Procédé selon la revendication 2, où le procédé est effectué sous une pression d'au
moins 1 bar, préférablement d'au moins 3 bars.
4. Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, où le procédé est effectué
à des températures de 15-100°C, préférablement de 20-80°C.
5. Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, où le procédé est effectué
avec ou sans solvant.
6. Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, où le procédé est effectué
en présence d'un catalyseur (préférablement un métal de transition sur un matériau
support, plus préférablement Pd/C).
7. Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, où le procédé est effectué
en présence d'un acide (préférablement HCl, H2SO4, acide p-toluènesulfonique).
REFERENCES CITED IN THE DESCRIPTION
This list of references cited by the applicant is for the reader's convenience only. It does not form part of the European patent document. Even though great care has been taken in compiling the references, errors or omissions cannot be excluded and the EPO disclaims all liability in this regard.
Patent documents cited in the description
Non-patent literature cited in the description
- STRICKLER et al.Helv. Chem. Acta, 1966, vol. 49, 2055- [0009]
- ERMAN et al.Tetrahedron, 1976, vol. 34, 2981- [0009]
